+ 86-15195999306 丨+ 86-25-83602718
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |
A plano-convex lens consists of a plane and a sphere, they are combined with other lenses to form an imaging system.
For infinite and finite conjugate applications, these lenses have a regular focal length and a shape close to the nearest profile.They can be used to focus collimating light or collimating point sources. In order to reduce the introduction of spherical aberration, the collimating light should be incident on the surface of the lens when focusing, while the incident light should be incident on the plane of the lens when collimating.
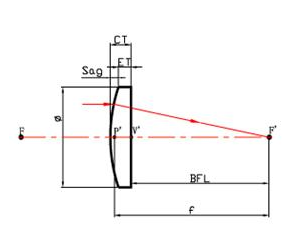
Basic Technical Parameters
Tolerance of Dimension: ±0.05mm
Surface Accuracy: 1/2λ,λ/4 per φ25.4mm
Centration:≥1′
Surface Quality: 60-40, 40-20, 20-10,10-5
Chamfer: 0.2-0.3mm×45°
Clear Aperture: >90%
Polish: High-precision Polish on Both Surfaces
Used in many applications, including telescopes, sights, magnifiers, light receivers, and concentrators.
A plano-convex lens consists of a plane and a sphere, they are combined with other lenses to form an imaging system.
For infinite and finite conjugate applications, these lenses have a regular focal length and a shape close to the nearest profile.They can be used to focus collimating light or collimating point sources. In order to reduce the introduction of spherical aberration, the collimating light should be incident on the surface of the lens when focusing, while the incident light should be incident on the plane of the lens when collimating.

Basic Technical Parameters
Tolerance of Dimension: ±0.05mm
Surface Accuracy: 1/2λ,λ/4 per φ25.4mm
Centration:≥1′
Surface Quality: 60-40, 40-20, 20-10,10-5
Chamfer: 0.2-0.3mm×45°
Clear Aperture: >90%
Polish: High-precision Polish on Both Surfaces
Used in many applications, including telescopes, sights, magnifiers, light receivers, and concentrators.